Female Pattern Hair Loss is more common than people think. With men, the hair loss is quite obvious. For women, Female Pattern Hair Loss presents with general thinning across the top of the scalp and may take years before it is quite evident.
What causes Female Pattern Hair Loss?
The exact cause of Female Pattern Hair Loss has not been delineated. Unlike Male Pattern Hair Loss, where excess of Dihydrotestosterone (a male hormone) has been shown to be the main causative factor, there has been no direct association with hormonal imbalances in women. In fact, most women with this condition have normal levels of androgens (male hormones). Female Pattern Hair Loss does worsen after menopause, giving some the theory that there could be a role for a relative decrease in oestrogen, and consequently relative rise of androgens, cause hair loss.
There is, however, an inheritance pattern. Like men, women can inherit Female Pattern Hair Loss from either their mother or father. The number of genes inherited will determine how thin the hair becomes.
Presentation of Female Pattern Hair Loss
For most women, they will find that their centre part will be wider than usual. In general, they will find that the top and crown of their scalp is quite thinned out. For some they may have a more “Male Pattern” type of hair loss, with thinning and recession to the temples. The staging system used is the Ludwig Classification:
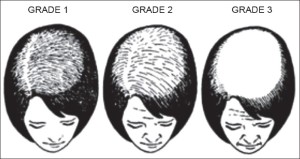
Next month : Treatment