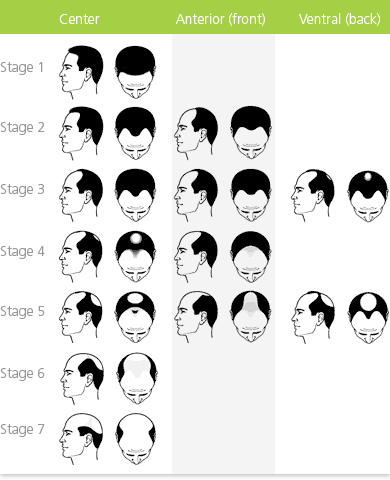
Treatment options for Male Pattern Hair Loss are quite limited. With more men seeking treatment, and plenty start suffering from hair loss at quite young ages, more research is being placed on reversing or slowing this frustrating condition.
Treatment of Male Pattern Hair Loss are mainly divided in to three: Topical, Oral, and Surgical
Topical Treatment of Male pattern Hair Loss
Topical Minoxidil
This is the mainstay of treatment for Male Pattern Hair Loss. Studies have shown that 5% Minoxidil prolongs the anagen phase and thickens the hair fibre. The exact mechanism by which it does this is still unknown. It takes 4-6 months before results can be seen. It is up to 60-70 % effective in the crown and 30-40% effective in the front of the scalp. The brand is Rogaine and it comes in 2 forms- solution and foam. There are many generic brands available and quite a few countries that provide it OTC.
In Europe, OTC caffeine based products are available in shampoo and lotion form. Caffeine has been shown to increase the anagen phase. The studies have been found to be encouraging.
Oral Treatment of Male Pattern Hair Loss
The two main medications used are Finasteride and Dutasteride. Both are used off-label from their intended use, which is for the treatment of Benign Prostatic Hypertension.
Finasteride (Propecia or Proscar) help to stop the conversion of Testosterone to Dihydrotestosterone by the enzyme 5 alpha reductase. Fiansteride takes up 4 months before results can also be seen. It has a slightly greater efficacy compared to Rogaine. Together with Minoxidil, there is increased benefit to the patient. Most persons can start off with Minoxidil and Finasteride added to see if there is any more improvement.
Dutasteride (Avodart) is a more potent form of Finasteride because it acts on the many forms of the enzyme. It is 95% effective compared to the 50-70% seen with Finasteride. However, it has 5 times more the effects of side effects compared to Finasteride. The main concerns for both Finasteride and Dutasteride include: decreased libido, decreased power of orgasm/ejaculation, erectile dysfunction, and depression. For Finasteride, this is quite low, but much higher in Avodart. The side effects usually go away after cessation of the medication, however, it should note that many men who start this medication are already at risk of having these issues.
Surgical Treatment of Male Pattern Hair Loss
The ultimate treatment of this condition is Hair Transplantation. It involves permanent removal of hair from the back of the scalp, which is less likely to be affected by the condition. These are then transplanted to the front of the scalp and will take and grow keeping their inherent properties from where they are coming from. There are two main types: Follicular Transplant (strip harvesting that leaves a visible scar) and Follicular Unit Extraction (individual harvesting of hair follicles). Hair growth is not immediate. It takes about 4-6 for the transplanted hairs to start growing, and up to a year for it to be noticeable.
Surgical treatment is limited to how much hair is present in the donor site. There are many factors that can cause decreased hair growth. However, up to 99% of the hairs transplanted usually grow.
Treatment of Male Pattern Hair Loss is limited but promising as there are many new treatment therapies such as Stem Cell Therapy are actively being investigated.
 \
\